Why Outsourcing To CDMOs Doubled In 13 Years
^ Biologics manufacturing has come to increasingly rely on biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing and development organizations (CDMOs) over the past 20 years.
^ The percentage manufactured exclusively in-house, for example, declined from 57.6% in 2006 to only 29.7% in 2023.
^ 8% of respondents will be “onshoring” their biomanufacturing in the next five years.
^ Over one-fifth (20.3%) indicated they will offshore a majority (over 50%) of their biomanufacturing operations to India, China, or another lower cost country over the next five years.
^ All of which is to say: Supply chain issues — whether they involve onshoring, transparency requirements, rated orders and export controls, or rerouting production due to drug shortages — will be critically important to the CDMO sector and its customers in the years ahead.
^ Another aspect of the “post-”COVID environment for CDMOs is: the rationalizing of manufacturing capacity. (Consolidation in the biotech industry is very much a possibility going ahead.)
^ Governments have gone back to bickering over healthcare spending and pay lip service to “preparing for the next pandemic”, while pharma manufacturing overall has been compelled to rationalize capacity.
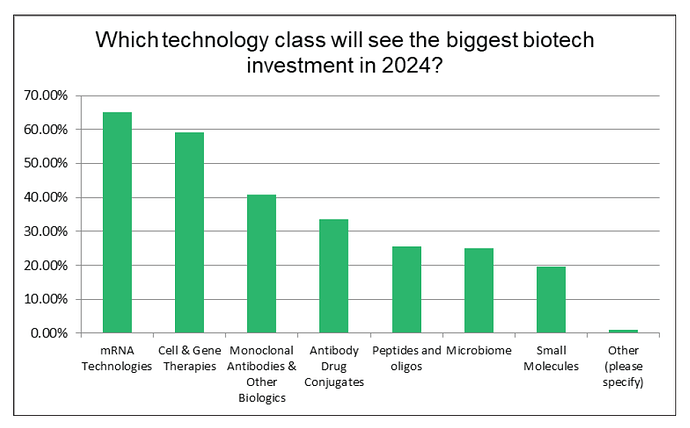
^ In the midst of all, there’s the promise of new/growing modalities: CGT, CAR-T, ADCs, mRNA and more.
^ The FDA approved significantly more biologic NMEs in 2022 than small molecule NMEs (24 compared to 17).
^ Another change affecting CMOs is that the most innovative therapies, which are often delivered by injection, have an even greater need for outsourcing – in part because these drugs require facilities that maintain sterility and other higher-value technologies.
Demand for Pharma Services & the Long-term Outlook
^ Over the past 10 years, the number of molecules in the R&D pipelines has more than doubled, with growth rates for small and large molecules around 5% and 12% CAGR respectively.
^ The split between small and large molecules in development pipelines is approaching 50-50 (which indicated more large molecules is being discovered).
^ The average drug taking over 10 years to go from discovery to commercialization.
^ One of the major contributors to growth in the CRO/CDMO sector is the emerging pharma/biotech community. By definition, these companies need to outsource most, if not all, of their R&D and manufacturing requirements.
^ 67% of overall contribution to Pharma Pipelines is by Emerging Biopharma while Large pharma has contributed 23%.
^ The number of companies with active R&D pipelines globally has grown from nearly 4800 in 2020 to over 5500 in 2023, while funding levels have dropped to nearly half the 2020 levels during the same period.
^ Big pharma is operating against backdrop of continuing inflationary pressures, rising capital costs, patent expiries, ongoing Federal Trade Commission (FTC) transaction scrutiny, and the impact of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the US.
^ Pharmaceutical companies are sitting on $700 billion for acquisitions and investment.
^ Both western and Indian CDMO’s is saying that the on-shoring momentum in India has been particularly consistent and strong over the past couple of years. That consistency has not been felt as much in the Western regions.”
^ The current funding/IPO climate in the emerging pharma is expected to sort out over next 12-18 months.
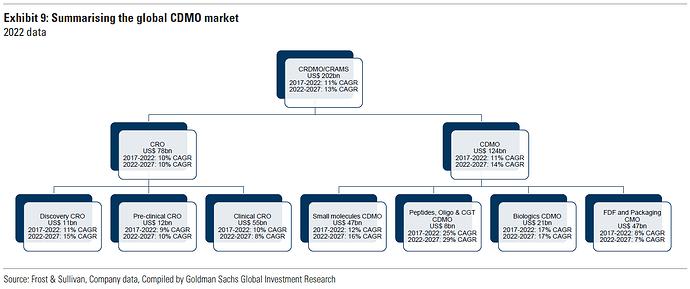
Trends Overview 2022-2027
^ Demand for biologics manufacturing capacity by volume is projected to reach nearly 4,400 kL, a 5-year growth rate of nearly 11.5% per year (just over 2,500 kL in 2022). In contrast Syngene has biologic capacity of 40,000L including Stelis capapcity.
^ Global biologics manufacturing capacity will increase to nearly 8,400 kL by 2027 from nearly 6,500 kL in 2023.
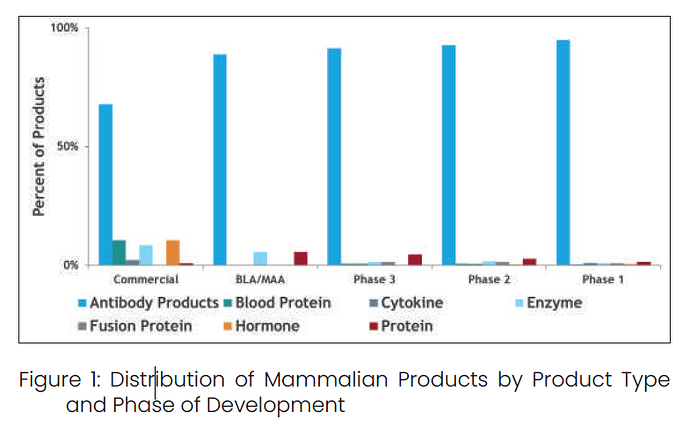
^ In 2022, the top five selling recombinant proteins generated nearly $71B in sales, four of which were antibody-based products (Humira, Keytruda, Stelara, Eylea) with sales totaling nearly $62B.
^ The fifth product, the microbially-expressed glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist Ozempic/Wegovy, posted just over $9B in sales. (A blockbuster drug approved by US-FDA to treat people with Type 2 diabetes, made by Novo Nordisk A/S. It has gained popularity for its off-label use, helping users drop excess pounds within a matter of months.)
^ Antibody related products CAGR was 16.9% from 2005 to 2015. Although this growth has remained in the low teens in recent years due to the maturation of many products and emerging alternative therapeutic modalities, it far exceeds the 4.5% growth rate of traditional pharmaceutical (i.e., small molecule) sales.
AN EMERGING TREND
^ Nutraceuticals, personal care and pharma are converging over the next 5-years, as the biology of health & wellness science accelerates.
^ Collagen is a classic example of an ingredient that has traditionally been applied topically as cream or powder, but we see many personal care companies now launching nutraceutical products with collagen combinations via a gastrointestinal route.
^ The global nutricosmetics market is expected to witness significant CAGR of 21% through to 2030, underscoring the potential of this evolving trend.
Where is CHINA?
^ The average cost per gram of primary recombinant proteins in China now (2023) is more than in the US ($294.00 in China to $255.29 in the US). This may be due, in part to, the rising demand and labor costs in China. (In reference, the labour cost in Syngene is 25-26%, which is ~35% of operating cost).
^ Multiple MNC pharma have closed their R&D centers in China. But they are leveraging China’s R&D workforce via other routes, such as co-development or licensing deals.
The BIOSECURE Act
^ It prohibits federal agencies & any other entity to use biotechnology equipment or service from a biotechnology company red flagged by the US govt. It also prohibits entering into a contract (with a third party) that will require the direct use of the biotechnology equipment or service from a biotechnology company that is red flagged.
^ As a result, companies that contract with any “biotechnology company of concern” could themselves become ineligible to receive federal contracts, loans, or grants.
^ The bill specifically targets WuXi AppTec (Shanghai, China), WuXi Bio (Jiangsu, China), BGI Genomics (Shenzhen, China), MGI (also Shenzhen), and MGI subsidiary Complete Genomics (San Jose, US) as major Chinese biotech and genomics companies that it alleges are affiliated with, or engaged in joint research with, foreign adversaries’ military, internal security forces, or intelligence agencies, and thus pose a threat to US national security.
Where is INDIA?
^ The 2022, mark a watershed moment in India’s rise in reputation of biologics production – notably, Covid vaccines, the Serum Institute, Bharat biotech, Biocon and, on the CDMO side, Syngene helping transform the country’s reputation.
^ The outlook for India into 2024 continues to look very strong and overall, the best of any market in the survey.
^ India is already supplying much of world generics demand: including 50% of drugs in Africa, 40% in the USA and around 25% in the UK, but what we are now seeing is a gradual shift in India toward high value drugs driven in part by the fact that there simply aren’t enough facilities in the west to support its innovation engine and desires to build these have cooled in an inflationary, low capital environment.
^ India is well known to have highly capable IT workforce and we may in fact see a** convergence of interest between India’s two largest export industries (pharma and IT).**
^ India has by far the world largest ‘naive patient’ base for clinical trials. This coupled with the country’s prestigious pharmaceutical manufacturing could indeed be an incredibly attractive combination for many of the world’s largest innovators.
^ India’s stellar IT prowess positions it as a potential leader in AI driven pharma innovations. With the world’s most extensive ‘naive patient’ base for clinical trials, the confluence of India’s pharmaceutical and IT sectors could make it a global epicentre for secondary data analysis using AI.
^ India to continue to invest in newer biologics technologies is that** CDMOs here are typically operating EBITA margins as high as 35% verses just 20% in the west.**
^ Majority of analysts state that on average biosimilar development takes just 3-5 years in India verses 7 in the West and costs on average 10X less – with prices as low as £10million in some cases.
^ India will now see the fastest rates of overall growth in biologicals in the next 5-years.
^ The extent of CDMO outsourcing in India is estimated to be 35-40% in the Pharma industry in FY23.
UPCOMING EXPANSION
^ AURIGENE PHARMACEUTICAL services, a subsidiary of Dr Reddy’s Laboratories is spending $40mn.
^ Divi’s Laboratories is building a factory over 500 acres.
^ Laurus Labs, is in the middle of a ₹990 crore expansion.
^ Jubilant Pharmova, is expanding in North America — it is spending $370 million in Spokane and Montreal to double sterile injectables capacity.
^ Kemwell has built a world-class facility in Bangalore and made India an emerging hub for cell therapy development and manufacturing.
^ Aragen is setting up a $30 million facility in Bangalore.
^ Aurobindo’s CuraTeQ Biologics is entering contract manufacturing operations for biologicals and building a ₹300 crore facility.
**^ The $42 billion domestic pharmaceutical industry has 3,000 companies with 10,500 manufacturing units. Of them, at least 100 are becoming CDMO specialists, an emerging segment that includes API manufacturing and contract research and development. **
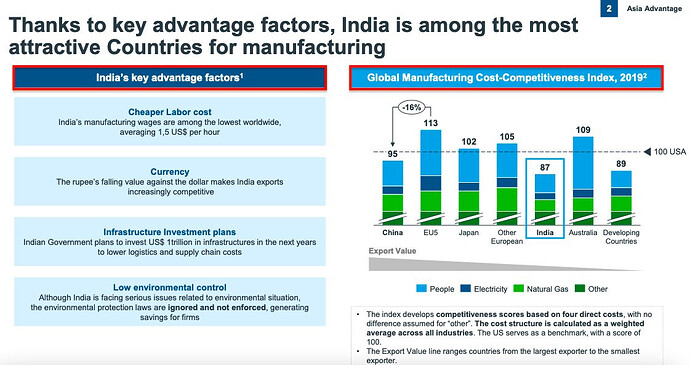
^ India’s ability to develop drugs at 1/4th the cost in the West and largest number of US FDA-approved plants outside U.S.
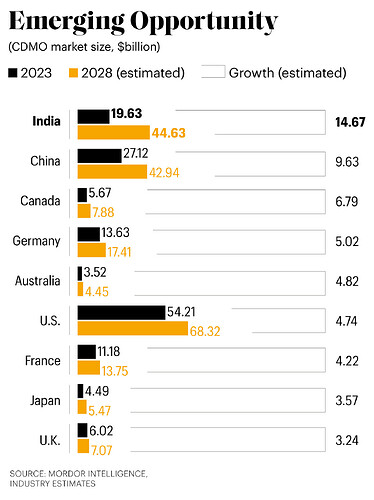
^ Global CDMO market was valued at $224.6 billion in 2023. Various industry estimates say Indian CDMO market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.67% from $19.63 billion in 2023 to $44.63 billion by 2029 by tapping API and contract research opportunities.
^ Global CDMO growth is projected at 6-7% over next five-six years.
^ Supply chain diversification (from EU, U.S. & China), increase in strategic and PE investments in world-class infrastructure, availability of skilled talent and management attention have led to a positive outlook for the CDMO space.
^ PLI Scheme for pharmaceuticals, launched in 2021 with an initial outlay of ₹15,000 crore over six years. It’s expected to attract investments of ₹17,425 crore. Also, PLI Scheme for bulk drugs, with an outlay of ₹6,940 crore, will boost production of 41 critical bulk drugs. Many companies started building bulk drug parks in India after government allowed 100% FDI in the sector.
^ It takes at least three-five years for big pharma players for evaluation of facilities, work culture and manufacturing systems before they award a major contract to companies in India.
In CONCLUSION,
^ The global CDMO landscape is undergoing a profound transformation driven by shifting market dynamics and the pursuit of innovative risk-sharing partnerships, in part driven by new innovative therapies.
^ Currently the CDMO space is going through funding winter & lack of govt support.
^ The sudden spurt in the Biotech companies seen during the COVID period is going through consolidation through M&A, which will probably last for 1-2 year.
^ Post that (Probably 2027) only any meaningful growth will be seen in the surviving entities.
^ CDMO companies based out of India has some inherent advantage, like low wages, Govt PLI for Pharma, improving infra & low cost of setting up the manufacturing facility.
^ Increasing number of drugs are coming from biologics than Small molecules.
^ Among the biomolecules, antibodies are seeing greater traction.
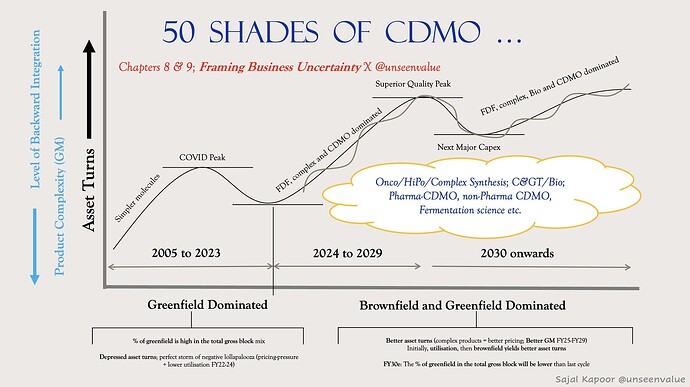
Future of CDMO
Pic Credit: Sajal Sir (Unseen Value)
Src:
1.
2.
3.
CPHI Annual Report-2023.pdf (2.4 MB)
4.
Seeking wisdom in the Indian Stock Markets | SOIC
5.
6.
https://twitter.com/punitbansal14/status/1763062560327139814?t=kionSUICd89UZtTvR5tZXw&s=19
7.
https://x.com/punitbansal14/status/1761713163551072335
8.
India_Healthcare_-_GS.pdf (1.1 MB)
| Subscribe To Our Free Newsletter |