I am sharing few notes on Knowledge Marine, i feel it has good growth ahead, but as investors what we need is good price and patience.
Business
The company is engaged in the business of dredging and hiring marine craft for various essential services to the major and minor ports across the coastline of India and neighboring countries. Dredging currently contributes ~95% to the total business.
Dredging – Dredging is the process of excavating or removing sediment, debris, or other material from the bottom of bodies of water like rivers, lakes, harbors, or the ocean floor. This is typically done using specialized equipment such as dredgers, which may be floating vessels or land-based machines equipped with mechanisms like suction devices or buckets.
Maintenance dredging vs capital dredging
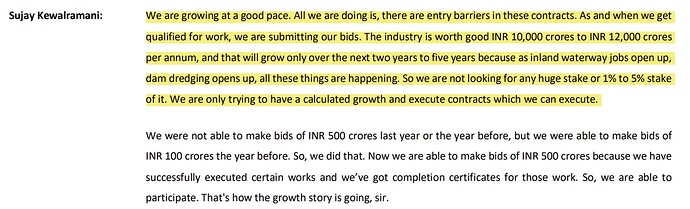
- Growth in the order book
End of Q4FY22 – ₹182 crore. H1FY23: ₹208 crore. FY23: ₹202 crore. H1FY24: ₹670 crore. H2FY24: ₹733 crore. Pipeline in ₹1,200 crore with ~40%-50% order win rate.
The company is increasing its qualification for orders as within 2 years it is now able to bid for orders worth ₹300 crore from being able to bid only for ₹100 crore orders.
- Increase in number of vessels
FY21: 4 vessels, FY22: 8 vessels. H1FY23: 10 vessels. H1FY25: 24 vessels. Aims to have 50 vessels within 10 years.
- Competition
“The job is not very easy, it requires a lot of skill. Also, you said the competition is not very high, the large players are the Government of India Dredging Corporation of India and there are players from Europe such as Van Oord, Boskalis, Dredging International, Jan de Nul; they choose to fix contracts which are easily above Rs. 100 Crores, Rs. 150 Crores so there is very minimalistic competition for the contract which are below ₹100 Crores.”
-
Competitive advantages
The reason the company is better than its closest competitor – Dredging Corporation of India -
How a company manages to keep its capex low?
-
Entry barriers as per the management
-
How the company manage to get 50% of its order?
-
Collection of data
-
Market size
-
Increase in debt, keeping cash to get better deals
-
Reason for decline in revenue in FY24
-
Capital allocation
“We have chosen the joint venture route to avoid the capex that is usually required to start these ventures. We have tried to keep our capex low and we have tried to have higher margins, so what you are thinking and saying is correct.” -
Future Outlook
Will exhaust ₹300 crore of order book. Orderbook at the end of FY25 might be close to ~₹1,200 crore
Management guidance:Revenue reaching ₹275-₹300 crore orderbook. Operating profit margins to be within 30%-50%. PAT reaching ₹60 crores.
Currently has over ₹700 crore orderbook which can be executed within 2-3 years.
Risks
-
Equipment and execution: By the nature of the business, when the company receives the order, the revenue is known. The margins then completely depend on the company’s execution skills and selection of the correct equipment. These two factors can decide margins and customer satisfaction. Good execution is needed for repeat orders, new orders, and protecting & improving operating margins.
-
Management stake selling: The management has sold a significant stake which was bought by a mutual fund. Further stake selling and a decrease in management holding is a significant factor to watch out for.
-
Moderate scale of business: Though revenue has increased to Rs 201.5 crore in fiscal 2023 from Rs 61.2 crore in fiscal 2022, it continues to remain modest. Modest scale limits pricing power with suppliers and customers and limits the benefits related to economies of scale. The revenue is dependent on achieving a healthy order book and timely execution of orders.
-
Tender-based nature of business: The company operates in a tender-based industry, which has predefined criteria for track record and physical infrastructure. Business certainty depends on timely order execution, which in turn relies on various external factors such as customer clearances and any change at their end.
Few questions on first look
-
Debt – They have raised debt to increase cash on balance sheet. This cash they will be using to acquire ships from second market whenever they win the order. Having cash ready gives them a better terms on the deal.
-
Fixed assets – These are the vessels they acquire for executing their orders. Number of vessels have increased to almost 20 in FY24 as compared to 10 in FY23.
-
H2FY24 decline – They had to evacuate from Myanmar due to GOI’s orders. ₹70 crore of revenue got delayed, expected to come this year.
-
The 55% margin thing was one off. They are guiding for 30%-40% margins. They have secured a sand mining contract in Bahrain. To enter this market, they have reduced their margin for the first order. Next orders in the region will have 35% margins.
About Sagarmala
The Sagarmala Programme, a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, represents an approach by the Government of India to transform the country’s maritime sector. With India’s extensive coastline, navigable waterways, and strategic maritime trade routes, Sagarmala aims to unlock the untapped potential of these resources for port-led development and coastal community upliftment. Approved by the Union Cabinet in March 2015, Sagarmala seeks to enhance the performance of the logistics sector by reducing logistics costs for both domestic and international trade.
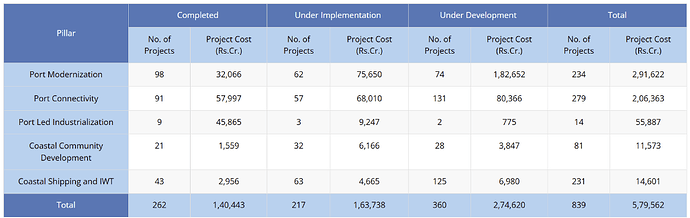
Overall, currently there are 839 projects worth investment of ~Rs. 5.8 lakh Cr. for implementation under the Sagarmala Programme by 2035. These include projects being implemented through various funding arrangements including Equity, Internal Resources, Grant in Aid, PPP mode etc. Out of which, 262 projects worth ~Rs. 1.4 lakh Cr. have been completed and remaining projects are under various stages of implementation and development.
| Subscribe To Our Free Newsletter |